
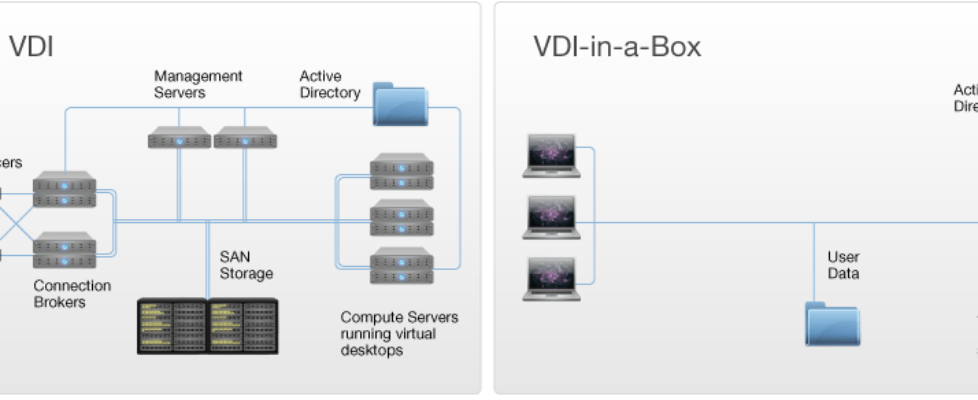
Non-persistent VDI usually simpler and cheaper, since there is no need to maintain customized desktops between sessions. Non-persistent: This type of VDI consists of desktops that revert to their initial state after the user logs out.At result, user is able to personalize the desktop for his/her needs since changes are saved even after the connection is reset. Persistent: This type of VDI is customized for a specific user, and the user can log in to the same desktop each time.VDI facilitates secure and convenient remote access that helps boost employee productivity. In the past, its high-performance requirements made it costly and challenging to deploy on legacy systems. The following are some of the needs of many organizations in the process of doing their work and projects: These applications are the technology used to create a virtualized application image and replicate it to all the virtual desktops in a desktop pool. Application Virtualization: VMware ThinApp is an example of Application Virtualization.For instance, departments like accounting and IT in an office might use desktops with different applications and configuration. Desktop Pools: These pools are a group of similar desktops that can be configured according to a specific function.When a user disconnects desktop, Connection broker updates the status to inactive. Connection Broker: When a user sends a request to connect to a desktop, Connection broker provides the user with an idle desktop instance.Hypervisor: Learn about hypervisor in here.Virtualization: Read about Virtualization in here.Independent Computing Architecture (ICA).It’s time to point out what protocol each vendor uses to set up and manage the session between end users and the virtual machine: Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS).Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops (formerly called is XenDesktop).There are three major products in the VDI market: Users connect to their desktop instances through their PCs or their thin-clients. Users can access these virtual desktops from any device or location, and all processing is done on the host server. How to implement VDI and how to use it? A hypervisor segments physical servers into virtual machines that in turn host virtual desktops. It is a form of desktop virtualization, as the specific desktop images run within virtual machines (VMs) and are delivered to end clients over a network. The virtual desktop image is delivered over a network to an endpoint device, which may be a traditional PC, thin client device or a mobile device. In fact, VDI is a desktop virtualization technology wherein a desktop operating system (OS) – typically Microsoft Windows – runs and is managed in an on-premises or cloud data center. Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) is defined as the hosting of desktop environments on a central server.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
